News
April 18, 2024
Mitsubishi Materials Corporation
Received the Science and Technology Award (Development Category) for the First Time in 2024 Commendation for Science and Technology by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
Five employees of Mitsubishi Materials Group have received the Science and Technology Award (Development Category) in 2024 Commendation for Science and Technology by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology for their research entitled "Development of a high-performance copper alloy for automotive terminals using an innovative alloy design method." This is the first time our company has been awarded in the Development Category.
This award selects individuals from all fields in Japan who have made outstanding achievements in R&D and have promoted understandings of science and technology, and is awarded to those whose innovated R&D or inventions have been put to practical use and contributed to the improvement of the social economy and the lives of the people of Japan.
The copper alloy that utilizes this awarded method, MSP®5, is a high-performance copper alloy for automotive terminals with the highest strength-conductivity balance among copper alloys, and has been produced full scale since April of 2021. With the electrification of automobiles constantly rising the performance requirements of terminals, many customers, including automobile parts manufacturers, are praising the high performance and reliability of MSP®5.
Mitsubishi Materials Group established "For people, society and the earth, circulating resources for a sustainable future" as "Our Commitment." We will continue to strength the expansion of resource recycling and enhancing the supply of high-performance materials and products by applying the results of the research in order to realize new copper materials and fulfill Our Commitment.
[Award Summary]
- Name of Achievement
"Development of a high-performance copper alloys for automotive terminals using an innovative alloy design method" - Recipient
- Yuki Ito (Mitsubishi Materials Corporation)
- Kazunari Maki (Mitsubishi Materials Corporation, Ph.D., Engineering)
- Takanori Kobayashi (Goto Seisakusho Co., Ltd.)
- Hirotaka Matsunaga (Mitsubishi Materials Corporation)
- Shinichi Funaki (Mitsubishi Materials Corporation)
- Yuki Ito (Mitsubishi Materials Corporation)

Award Ceremony
(Recipient: From left: Kobayashi, Ito, Maki, Matsunaga, Funaki)
Received a certificate of commendation
from Masahito Moriyama,
Minister of Education, Culture, Sports,
Science and Technology - Award Details
As CASE progresses in automobiles, automotive components are becoming multifunctional, and the number of automotive terminals in a connector is increasing. As a result, there is a demand for smaller automotive terminals, and to accomplish such miniaturization requires copper materials with higher strength, electrical conductivity, and heat resistance, while maintaining formability.
The development takes advantage of the superior characteristics of solid solution alloys (*1), and vastly improves upon conventional properties using an innovated alloy design method that focuses on solid solution strengthening by supersaturation (*2) and highly effective alloying element magnesium (Mg) to design a new high-performance copper alloy and to establish mass production technology. An additional feature of this technology is its low specific gravity compared to conventional material due to supersaturating light weight Mg and utilizing its expansion effect on copper's crystal lattice. Light weight also contributes to reduction in the amount of copper used in products and in the material cost.- (*1)
- The formation of an alloy by dissolving (solid solution) foreign atoms (solute atoms) into the host phase (solvent atoms).
- (*2)
- Solid solution strengthening is a method of strengthening a material by dissolving (solid solution) foreign atoms (solute atoms) into the host phase (solvent atoms). A supersaturated solid solution is an alloy where solute atoms are dissolved in excess compared to normal solid solution.
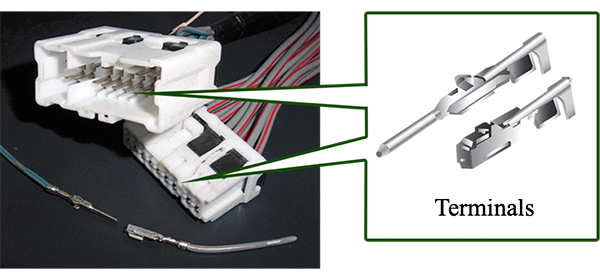
Automotive connectors
Press-fit terminal for automotive
Application examples of high-performance copper alloy "MSP®5"
for automotive terminals that utilized the awarded method
[Related Releases]
April 21, 2021
Start of Full-Scale Production of Copper Alloy "MSP5" for Automotive Small Terminals
URL: https://www.mmc.co.jp/corporate/en/news/2021/news20210520.html
June 1, 2022
Proprietary Copper Alloy MSP5 Received 2021 Technology Award from the Japan Copper and Brass Association
URL: https://www.mmc.co.jp/corporate/en/news/2022/news20220609.html
[Past Awards Related to the Awarded Research]
- 48th Paper Award in 2014
"Properties of High-Concentration Cu-Mg Solid-Solution Alloys as Materials for Terminals"
The Copper Institute of Japan - 39th Technology Development Award in 2016
"Development of MSP5, a High Strength and High Electrical Conductive Solid-solution Copper alloy for Automotive Terminal"
The Japan Institute of Metals - 68th Japan Mining Industry Association Award in 2017
"Development of MSP5, a copper alloy for automotive terminals"
Japan Mining Industry Association - The 52nd Best Paper Award in 2018
"Evaluation of dislocation characteristics affecting tensile elongation of solid-solution copper alloys"
The Copper Science Society of Japan - FY2021 Technology Award in 2022
"Development of MSP®5 Copper Alloy for Small Automotive Terminals"
Japan Copper Products Association
[Papers and other documents]
- "Solid-solution copper alloys with high strength and high electrical conductivity,"
Scripta Materialia, vol. 68 p777~780, published in 2013
URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S135964621200810X - "Effect of Plastic Deformation on the Proof Strength and Electrical Conductivity of Copper-Magnesium Supersaturated Solid-Solution Alloys,"
Materials Transactions, vol. 55 p1738~1741, published in 2014
URL: https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/matertrans/55/11/55_M2014220/_pdf/-char/ja - "Properties of High-Concentration Cu-Mg Solid-Solution Alloys as Materials for Terminals,"
(Received the 48 Thesis Prize of the Japan Copper Society) Copper and Copper Alloys, vol. 53 p198~202, published in 2014 - "Characterization of Microstructural Evolution in Cu-Mg Alloys Induced by Stress Relaxation by Using X-ray Diffraction Line-profile Analysis,"
Copper and Copper Alloys, vol. 55 p202~207, published in 2016 - "Effects of Microstructural Characteristics on Stress Relaxation Resistance of Solid-Solution Strengthening Copper Alloys,"
Copper and Copper Alloys, vol. 56 p45~50, published in 2017
- "Evaluation of dislocation characteristics affecting tensile elongation of solid-solution copper alloys"
(Winner of the 52 Thesis Prize of the Japan Copper Society), Copper and Copper Alloys, vol. 57 p18~24, published in 2018 - "Development of High-Strength Solid-Soluble Cu-Mg Alloys for Small Terminals,"
Journal of Japan Institute of Copper, vol. 60 p262~265, published in 2018
<Contact details for inquiries>
Corporate Communications Dept.: +81-3-5252-5206