News
October 31, 2023
Mitsubishi Materials Corporation
National Institute for Materials Science
Property Prediction Model Built for Copper Alloys
- Supporting the Superiority of Mitsubishi Materials' Magnesium-Copper Alloy MSP™ Series -
Mitsubishi Materials Corporation ("MMC") and the National Institute for Materials Science ("NIMS") have developed a new property prediction model for copper alloys with an exhaustive range of 86 elements. The results of the two organizations' joint research using this model revealed that magnesium (Mg) is the best overall element to be added to copper.
MMC and NIMS established the MMC-NIMS Center of Excellence for Materials Informatics Research in 2020 and have been engaged in research on data-integrated materials development systems. The joint research is achieved by combining MMC's copper alloy design and simulation technologies with NIMS' strength in "data-driven approach", a materials development method using data science.
For copper alloys, which are difficult to subject to real experiments from the viewpoint of stability, cost, and safety, the research used a combination of simulation technology and the data-driven approach to build a property prediction model capable of accurately predicting copper alloy properties, and compared various additive elements added to copper. As a result, it revealed that magnesium (Mg) is the best overall additive element to be added to copper. This demonstrated the superiority of the properties and quality of the MSP™ Series (*), MMC's Cu-Mg solid-solution strengthened alloys.
- (*)
- Solid-solution strengthening: A technique of dissolving foreign atoms (solute atoms) into the matrix (solvent atoms) to strengthen the material.
Mitsubishi Materials and NIMS will continue to contribute to the improvement of the international competitiveness of the entire Japanese materials industry by deepening inter-organizational cooperation and promoting the dissemination and utilization of the obtained results.
[Overview]
Research background and description
MMC developed the MSP™ Series of Cu-Mg solid-solution strengthened copper alloys with excellent balance between mechanical and electrical properties and has been promoting product rollout. The development of the MSP™ Series confirmed the superiority of magnesium (Mg), with its low environment-impacting solid-solution process, and having superior properties compared to conventional alloys such as brass and bronze without having the toxicity such as that of beryllium (Be).
However, in view of the possibility of the existence of other potential additive elements, experimental data, material property prediction formulas, and the data-driven approach were computationally integrated to build a property prediction model for copper alloys that covers elements from hydrogen with atomic number 1 to radon with atomic number 86. Additionally, a Figure of Merit (FOM) was newly derived for this research to evaluate the balance between mechanical and electrical properties of copper alloys, allowing for the property balance to be evaluated based on the size of FOM.
Research results
Figure 1 shows the prediction results of mechanical and electrical properties using the property model. The lower right direction of the plot indicates suppressed increase in resistivity with increase in mechanical strength, represents superior balance, with a large FOM, denoting the superior alloy.
Using the FOM, solid-solution copper alloys were ranked by their combination, shown in the result below.
- 1st: Cu-Ag (silver-copper alloy)
- 2nd: Cu-Cd (cadmium-copper alloy)
- 3rd: Cu-In (indium-copper alloy)
- 4th: Cu-Hg (mercury-copper alloy)
- 5th: Cu-Au (gold-copper alloy)
- 6th: Cu-Mg (magnesium-copper alloy)
Solid-solution copper alloy ranking
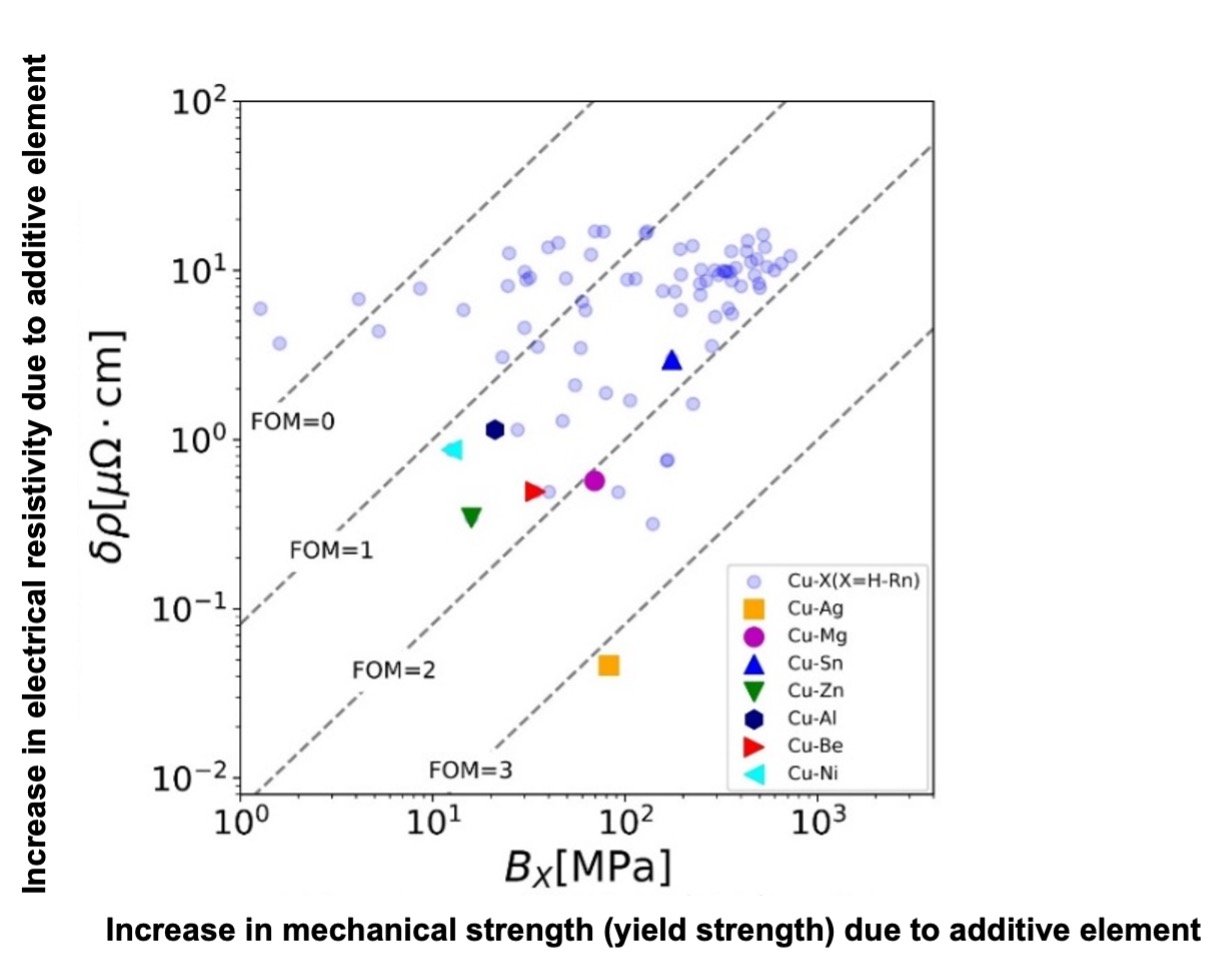 Figure 1. Relationship between mechanical and electrical
Figure 1. Relationship between mechanical and electrical properties of solid-solution copper alloys
As the alloys ranked from 1st to 5th contain high-cost elements (Ag and Au) and toxic elements (Cd, In, and Hg), it was confirmed that Cu-Mg is the solid-solution copper alloy that satisfies the three points of property balance, cost, and safety.
Cu-Mg alloys have been commercialized as MMC's MSP™ Series and the research results support the high properties and quality of this series of products. Furthermore, as this research assumed the simplest form of alloy, a solid-solution copper alloy composed of two elements, and conducted comprehensive comparisons for almost all of the elements on the periodic table, the results will be very useful for future solid-solution copper alloy development.
<Research paper>
The research has been published in the Science and Technology of Advanced Materials: Methods, an international academic journal, in September 2023.
- Title
- Comprehensive elemental screening of solid-solution copper alloys
- Authors (MMC)
- Kenji Yamaguchi, Takuya Ishigaki, Yuki Inoue,
Shuhei Arisawa, Hirotaka Matsunoshita,
Yuki Ito, Hiroyuki Mori, Kenichiro Suehiro, Kazunari Maki - Authors (NIMS)
- Kenji Nagata, Masahiko Demura
<Contact details for inquiries>
MMC:
Corporate Communications Dept., Strategic Headquarters
+81-3-5252-5206
NIMS:
National Institute for Materials Science
Public Relations Office
+81-29-859-2026