News
April 21, 2022
April 13, 2022
Mitsubishi Materials Corporation
Start of Development of a "Thermal Conductive Putty" Material Softer than Thermal Conductive Rubber
- Applying the Technology for Clay-Like Thermal Conductive Material Capable of Adhering to Complex Shapes -
Mitsubishi Materials Corporation has begun development of a "thermal conductive putty" as a thermal conductive material to be sandwiched between high-temperature components, such as lithium-ion battery modules and electronic circuit boards, and low-temperature heat-dissipating components, such as heat sinks, to facilitate heat transfer from the former to the latter components.
Interfacial thermal resistance (thermal resistance generated on the contact surface) is generated on the contact surface between the high-temperature and the low-temperature components, which hinders heat transfer from the former to the latter components. Due to this interfacial thermal resistance, high-temperature components cannot be sufficiently cooled, which poses a problem. Thermal conductive rubber sheets are used as a countermeasure, but they have proven to be inadequate for solving the problem because, while they can be deformed to some extent according to the shape of the components they are in contact with, it is difficult to make them adhere closely enough.
To overcome this problem, we worked to develop a thermal conductive material that is both thermally conductive and softer than rubber and succeeded in creating technology that combines a filler having high thermal conductivity with a particular rubber to create a soft clay-like thermal conductive material. By applying this technology, we will advance the development of a "thermal conductive putty" that can closely conform to the shape of components it is in contact with to achieve closer adhesion.
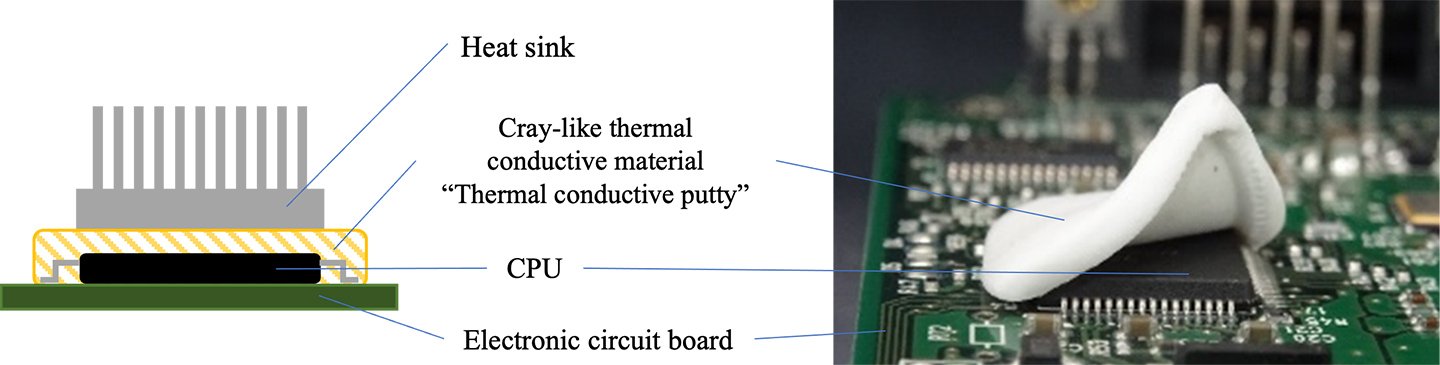
Example of use of "thermal conductive putty"
: Conceptual diagram of a measure for preventing CPU heat generation
Features of "thermal conductive putty"
- The clay-like softness provides the ability for it to adhere to components more closely than conventional rubber sheet-type thermal conductive sheets. The material reduces the interfacial thermal resistance generated at the contact surface between the respective component and the "thermal conductive putty", facilitating efficient heat transfer.
- Compared with conventional thermal conductive sheets, the clay-like quality allows the reaction force from parts being held down to be reduced. In addition, silicone is not used, hence it does not contain any ingredient that may cause defective electrical relay contacts (low-molecular-weight siloxane).
At present, heat generation is an issue in a wide range of fields such as automotive and electronic equipment, and demands for thermal conductive materials are increasing. We will continue to work on further development so as to be able to make better proposals to meet these demands.
The vision of the Mitsubishi Materials Group is to "become the leading business group committed to creating a sustainable world through materials innovation, with use of our unique and distinctive technologies" based on its corporate philosophy of "For People, Society and the Earth." Mitsubishi Materials will continue to help build a prosperous society through developing and providing nonferrous metal materials and high-value-added products.
<Contact details for inquiries>
Corporate Communications Dep., Management Strategy Div.,
Strategic Headquarters+81-3-5252-5206