- Home
- Investor Relations
- Management Policy
- Business and Other Risks
Business and Other Risks
-
1. Process for identifying critical risks
The Group comprehensively identifies and evaluates significant management and operational risks each fiscal year through its Executive Officers and head office management divisions, considering social conditions, the business environment, and the Group's management challenges. In addition, significant business-specific risks are identified and assessed each fiscal year by the head office management divisions, and decision-making on said risks is carried out through the Sustainability Deliberative Council in which all Executive Officers participate.
-
2. The Group's risk management system and operation status thereof
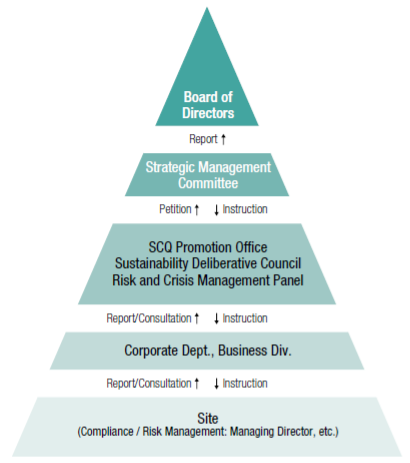
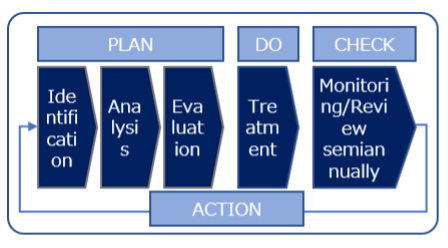
In addition to the above critical risks, the Group identifies and evaluates the risks specific to each business site, formulates implementation plans for each site, and conducts risk management activities. The status of activities is monitored and reviewed on a semi-annual basis through the Sustainability Deliberative Council and other meetings, and the results are reported to the SCQ Promotion Office and the Strategic Management Committee, while the risk status is monitored and reviewed by upper management. Furthermore, critical risks are reported to the Board of Directors, which oversees the overall risk status, including risk management (see Figure 1).
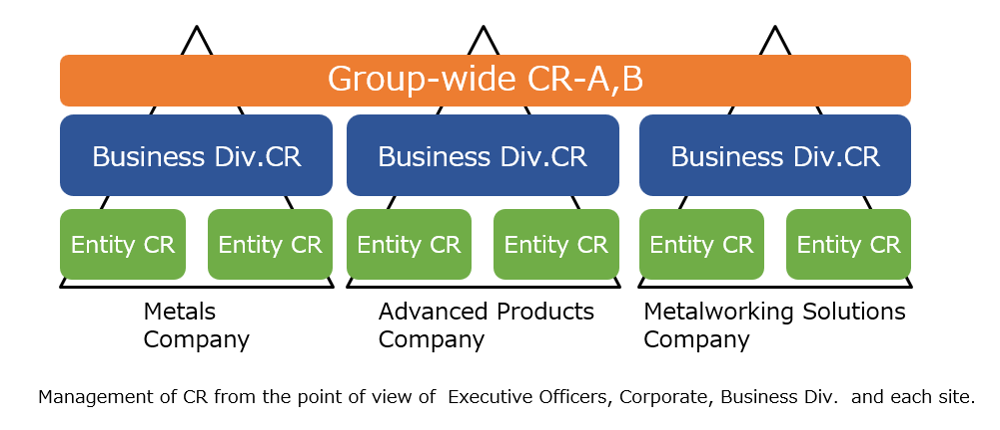
We classify major risks as Group-wide risks, business-specific risks (risks that have a significant impact on the overall operation of specific business), and business-site-specific risks (risks that have a significant impact on the operation of specific sites), and the roles to be played by each organizational position level (planning, implementation, support, and monitoring/review) are clearly defined (see Figure 2). Specifically, the management and business divisions at the head office communicate semiannually with business sites to ensure the implementation of countermeasures at business sites, share information on the implementation status and issues, and provide necessary support after discussions (see Figure 3).
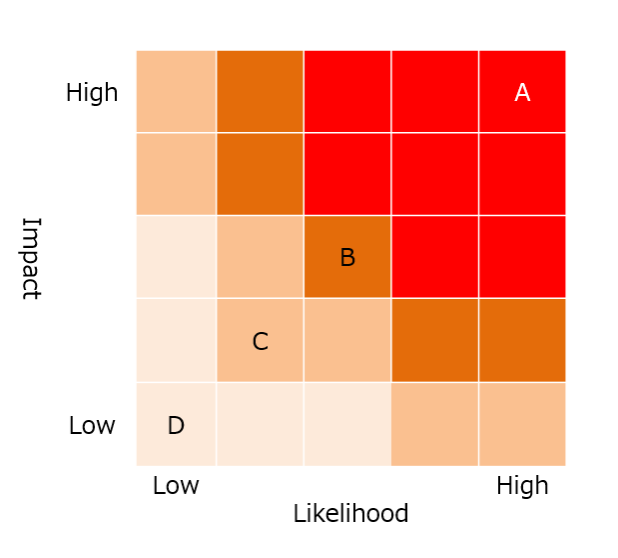
Additionally, we develop scenarios for each critical risk and conduct quantitative and qualitative assessments of their impact and likelihood of occurrence based on standardized assessment criteria, thereby creating a concrete image of the impact risks will have if they occur, which is shared throughout the Group (see Figure 4).
-
3. Business and other risks
The Group identifies sustainability issues to realize both "our own sustainability," which refers to the Group itself remaining sustainable, and "environmental and social sustainability," which refers to ensuring environmental and social sustainability through our business activities. We believe that by appropriately addressing sustainability issues, we can enhance our corporate value by realizing both economic and social value, and reduce various risks within the Group.
Based on the above, the Group's management has identified the following as the Group's sustainability issues and critical associated risks.
The following does not cover all the risks of the Group. In addition, this section contains forward-looking statements based on our assessment as of June 24, 2025.
-
(1) Promotion of resource circulationLikelihood of occurrence: High; Impact: Large
As the world's population and economy grow, environmental issues such as an increase in resource and energy consumption, a rise in the amount of waste, and global warming are becoming increasingly serious. Going forward, the linear economic model of mass production, mass consumption, and mass disposal may no longer be viable, and the risks associated with raw material procurement, including resource depletion, and the difficulties of waste disposal may increase.
Accordingly, there is a need to shift from a society that continues to consume limited resources to one that reduces waste generation and recycles resources for effective use. If we do not promote resource recycling in each of our businesses, it could lead to a loss of growth opportunities and a risk of exclusion from the industry.
In light of this situation, pursuant to the Medium-term Management Strategy for the period from the fiscal year ended March 2024 to the fiscal year ending March 2031, the Group aims to build a recycling system for metal resources based on our strengths and realize growth throughout the value chain by expanding the scope, regions and scale of our operations. We will promote resource recycling through our advanced recycling technologies for E-Scrap, home appliances, carbide tools, etc., which is one of our strengths, and develop and provide recyclable products to enhance resource circulation. By establishing and executing resource recycling strategies with a regional focus, especially in Europe, we aim to strengthen our competitiveness over the medium- to long-term.
-
(2) Strengthening measures to address global environmental issuesLikelihood of occurrence: High; Impact level: Medium
With regard to climate change, the global movement toward carbon neutrality is accelerating, and many countries, including Japan, have declared their commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050. If climate change policies and regulations are tightened and carbon pricing systems (emissions trading systems and carbon taxes) are introduced or intensified, the Group's business performance and financial position could be affected by the costs associated with GHG (Greenhouse Gas) emissions. Furthermore, in our initiatives to achieve carbon neutrality, we are also required to actively utilize renewable energy sources in the energy sector, and if we fail to take advantage of such opportunities to expand our business, we may miss out on growth opportunities for the Group.
In addition, there is a growing focus on nature-positive initiatives to halt and reverse the loss of biodiversity to put nature on a recovery path, and business activities with consideration for the natural environment are required.
The Group has set a goal of achieving carbon neutrality by the fiscal year ending March 2046, and as part of its GHG reduction targets for the fiscal year ending March 2031, the Group is working to reduce GHG emissions from its business activities by installing energy-saving equipment and expanding the use of renewable energy. In addition, to improve the market competitiveness of the Group's products, we are improving manufacturing processes, developing environmentally friendly products, and developing technologies to reduce environmental burden, such as CCUS (Carbon dioxide Capture, Utilization, and Storage).
Meanwhile, we expect that the reinforcement of policies and other measures related to climate change will increase demand for technologies, products, and services that contribute to energy conservation and GHG emission reductions, thereby expanding business opportunities. The Group is engaged in initiatives such as the development of materials, products, and technologies that contribute to decarbonization, the development and promotion of renewable energy sources such as geothermal power generation, the promotion of demonstration tests and technological development for CO2 capture and utilization, and conservation activities for the forests owned by the Group.
-
(3) Enhancement of human capitalLikelihood of occurrence: Medium; Impact: Large
Due to a declining workforce owing to falling birthrates and an aging population as well as diversification of individual needs in terms of careers and work styles, it is becoming increasingly difficult to secure human resources and to develop expert personnel over the medium- to long-term. In strengthening overseas business development, it is necessary to respect and collaborate with each individual while ensuring fairness and recognizing diversity in culture and values.
Under such circumstances, if measures to support flexible work styles and the design and operation of personnel systems, etc., are inadequate, employee engagement may decline and it may become difficult to secure the human resources needed for corporate growth.
Based on the belief that "employees are the source of new value creation and the Group's sustainable growth," we see talent as a form of human capital rather than just resources or sources of costs. We are strengthening our human capital through human resource policies that maximize the value of each employee and build a foundation for co-creation and growth through a diverse workforce.
In addition, the Group has business sites in Japan and overseas, as well as suppliers of raw materials and other materials in numerous countries and regions. If human rights violations (forced labor, child labor, harassment, discriminatory acts, etc.) were to occur in the Group's own operations or supply chain, it could not only affect production and procurement but also damage the Group's social credibility and reputation.
For this reason, the Group has established the Sustainability Policy, which clarifies our respect for internationally proclaimed principles of human rights based on the belief that respect for human rights is the foundation of our business activities, and has also formulated a Human Rights Policy to promote initiatives aimed at reducing such risks.
-
(4) Activation of communicationLikelihood of occurrence: Medium; Impact: Medium
Building relationships of trust through communication and dialogue with stakeholders such as shareholders, employees, customers, suppliers, local residents, NGOs, and government organizations, understanding their needs and problems, and applying them to corporate activities are important initiatives that are essential for enhancing corporate value. A decline in engagement with stakeholders may not only hinder the formation of appropriate stock prices but could also lead to a decline in employee motivation and compliance awareness, a loss of customer loyalty, and damage to the Group's brand.
In addition to formulating a policy for constructive dialogue with shareholders and investors and enhancing dialogue, the Group holds various briefings, collects and analyzes opinions from shareholders and investors, and provides feedback to the Board of Directors and top management.
The Group believes that increased employee engagement will lead to employees making the most of their abilities, which will result in increasing the corporate value of the Group. Additionally, we recognize that building an open organizational culture that is conducive to free and open communication strengthens governance and prevents compliance violations. Based on this, the Group strives to deepen communication between top management and employees through opportunities for direct dialogue and training.
To respond to the diverse needs of customers, the Group analyzes complaint information and conducts customer satisfaction surveys as part of its quality management activities. The Group takes customer opinions seriously, shares them with management, and reflects them in improvement measures to provide better products and services.
Furthermore, the Group has established the "Community Contribution Activity Policy" and actively engages in contribution activities to solve social issues, including efforts for diversity, equity, and inclusion (DE&I); nature conservation; next-generation education support; and minority support in each region, thereby working to coexist with local communities.
-
(5) Strengthening information securityLikelihood of occurrence: High; Impact level: Medium
The Group positions information security as one of the critical issues in terms of risk management. In particular, the Group recognizes the personal information of customers and business partners as one of the most important information assets, and works to reduce the risk of information leakage, loss, or damage. The failure of critical information infrastructure and networks, cyber-attacks (cyber-terrorism), and other unforeseen events, as well as the unauthorized removal of information, inadequate or poorly managed computer systems, and the leakage of personal information and other information due to computer viruses and malware, could lead to a loss of social credibility.
For this reason, to enhance IT global governance, including IT literacy, the Group appropriately invests in crucial information infrastructure and networks, updates equipment, and extends the usage period as necessary. In addition to strengthening IT asset management to prevent information leaks, we also implement effective security measures to reduce risk by promoting measures and enhancements in the four areas of governance, security improvement, predictive detection/early detection, and prompt response.
-
(6) Strengthening response to SCQ issuesLikelihood of occurrence: High; Impact: Large
If the Group pursues only earnings (E), disregards safety & health (S) at manufacturing sites, neglects compliance and environmental management (C), and supplies products that do not meet required quality standards (Q), it may lead to a decline in corporate value not only due to legal sanctions but also a decrease in social credibility.
To reinforce responses to SCQ issues, the Group has established the SCQ Promotion Office headed by the CEO and subcommittees consisting of the general managers of related departments, etc., to focus on the core aspects of corporate activities, such as "safety and health," "compliance," and "quality."
Concerning S, Safety & Health (safety and health first), we analyze the occurrence of occupational accidents within the Group, identify issues to be intensively addressed, and formulate specific measures. We also regularly share information on the progress of each measure and discuss solutions. In addition, we regularly hold meetings of safety managers and meetings of safety supervisors and safety instructors to exchange information on various accidents and safety and health activities within the Group, which spans a wide range of industries, thereby improving the level of safety and health. Furthermore, we position employee health management as an important management issue and have established the Health and Productivity Management Panel under the SCQ Promotion Office to implement a variety of measures for maintaining and promoting health throughout the Group.
As for C, Compliance & Environment (Compliance, Fair & Equitable Activities, Environmental Management), we consider compliance to be a broad concept that includes not only legal compliance but also corporate ethics and social norms, and we believe that we must faithfully meet the expectations of our stakeholders. With a view to strengthening the compliance system of the entire Group, we are continuing our efforts to raise the compliance awareness of every employee within the Group through various measures, including training in Japan and overseas. Further, by accurately and promptly collecting and sharing information on compliance violations that occur within the Group, we take appropriate measures against violations and reflect such information in risk management activities, education, and training to prevent recurrence. For the environment, in accordance with relevant laws and regulations, we strive to prevent air, water, and soil pollution. We conduct business activities in compliance with various environment-related laws and regulations concerning climate change, air pollution, water pollution, harmful substances, waste recycling, and soil and groundwater pollution. As environmental laws and regulations become stricter in Japan and overseas, to respond to revisions to laws and regulations and changes in environmental standards, we promote measures such as sharing information on revisions to applicable laws and regulations, providing thorough training and education, and promoting measures to avoid, reduce, and transfer risks, including strengthening facilities, throughout the Group.
Regarding Q, Quality (quality of products, services, etc. provided to "customers"), in order to thoroughly prevent the recurrence of a series of quality issues that occurred from November 2017, we continue to implement recurrence prevention measures, have established a Quality Review Day to prevent memories of quality issues from fading into the past, and engage in "proactive quality management," thereby creating a system to prevent the production of non-conforming products.
-
(7) Enhancement of sustainable supply chain managementLikelihood of occurrence: Medium; Impact: Large
In recent years, there have been frequent occurrences of supply chain disruptions and breakdowns on a global scale, including pandemics and natural disasters. Additionally, there are concerns that various national regulations on rare minerals will threaten the supply chains. Copper concentrates, the main raw material for copper smelting, are produced in limited regions around the globe. Resource-rich countries are increasingly campaigning against development due to policies to protect their own resources and heightened environmental awareness. Newly developed copper mines are required to mine at higher elevations and deeper areas, with lower grades and increased impurities. As a result, a lack of stable procurement of clean copper concentrates could lead to significant disruptions in the operations of copper smelters. As treatment charges and refining charges (TC/RC), which represent smelting margins, have recently declined significantly, the profitability of the smelting business is expected to deteriorate. In this context, shifting toward a smelting business centered on recycled materials and establishing a resource circulation loop at an early stage will also contribute to improving the profitability of the Group.
Moreover, there is a growing importance placed on resource recycling, and competition is expected to intensify, especially in the collection of recycled raw materials such as E-Scrap (waste substrates of various electronic devices), which contains high concentrations of valuable metals like copper, gold, silver, platinum, palladium, and other valuable metals. The Group has the technological superiority and advanced operational know-how of its proprietary copper smelting process (the Mitsubishi Process) and is building a global E-Scrap collection system and strengthening its processing capacity. However, if the Group cannot strengthen its stable procurement base for E-Scrap, there is a risk that the expansion of resource recycling, as detailed in the FY2031 Strategy, may stagnate.
To secure a stable supply of clean copper concentrates for the Group, the Mantoverde Copper Mine, in which we hold a 30% interest, commenced commercial sulfide ore production in 2024. Meanwhile, the Zafranal Copper Project, in which we hold a 20% interest, is in the process of conducting research and analysis for investment decisions. In April 2023, we participated in the Casino Copper Mine Project through equity participation in Western Copper and Gold Corporation.
To expand the Group's E-Scrap business, we invested in Exurban in the United Kingdom, which plans to build a new recycling plant in Indiana in March 2023. Exurban is dedicated to realizing the world's first zero-waste recycling plant specializing in E-Scrap and other recycled raw materials. Using this as a foothold, we aim to create opportunities to expand our metal resource recycling business in the U.S. and, in the future, to grow our business worldwide, including in Asia and Europe.
While globalization has led to economic development, supply chains have become increasingly complex. Hence, there is a possibility that we may not be able to identify human rights violations at our suppliers, such as poor working conditions, child labor, and forced evictions. In addition, legislation to mandate human rights due diligence has been introduced in European countries, such as the United Nations Human Rights Council's Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights and the United Kingdom's Modern Slavery Act. As such, companies are required to manage and address risks relating to human rights, and human rights risks have become a very important issue.
The Group understands that our business may directly or indirectly affect human rights in all areas of our business activities, from raw material procurement to the development, production, distribution, consumption, disposal, and recycling of materials and products. Accordingly, to ensure the effectiveness of the Group's Human Rights Policy, Procurement Policy, and others, we promote initiatives to respect human rights in the supply chain, such as conducting multilayered initiatives (including awareness-raising activities, due diligence, and securing relief measures) and maintaining (gold, silver, tin, tungsten) and implementing (copper, lead) responsible mineral procurement certification.
In addition, we are proactively enhancing our preparedness for unpredictable risks such as pandemics and natural disasters by developing an all-hazards business continuity plan (BCP) and other measures.
-
(8) Deepening of digital transformation (DX)Likelihood of occurrence: Medium; Impact: Large
Significant technological developments in IT, telecommunications, energy, and other sectors have brought profound change in the global economic landscape, and the rapid progress of digitization is transforming society. Under these circumstances, the use of digital technologies is essential for conducting business activities and enhancing corporate value. Failing to convert our analog operations to digital ones and transform our business through IT could potentially impair our Group's competitiveness.
The Group implements DX strategies (Mitsubishi Materials Digital Business Transformation (MMDX)) that serve as a foundation that enables us to prevail in global competition. We use data and digital technology to strengthen three key pillars of business, namely, business added-value, business operation competitiveness, and management speed.
-
(9) Pursuit of value creationLikelihood of occurrence: Medium; Impact: Large
To strengthen our competitiveness for the sustainable enhancement of corporate value, it is necessary to focus management resources on competitive businesses from a long-term perspective and create businesses and products through technological innovation, rather than merely temporarily increasing profit margins through the reduction of labor and other costs. Without promoting the pursuit of value creation, including medium- and long-term growth investments, our Group's competitiveness may be undermined.
In pursuit of value creation, the Group is working to build a competitive advantage that leads to profitability by strengthening our manufacturing capabilities, marketing skills, and sales force, enabling us to generate profits even in a challenging external environment. Additionally, we are implementing measures to realize new business ideas more quickly and reliably by accelerating business development through the use of external resources and by combining investment and financing strategies, such as M&A and equity investment.
-
(10) Geopolitical and geoeconomic risksLikelihood of occurrence: High; Impact: Large
The Group has production and sales sites, and others in 32 countries and regions overseas, and positions its overseas business as an important foundation for the growth of the Group's business.
In the event that geopolitical risks such as political instability, conflicts between nations, unilateral invasions, or political upheavals materialize in the countries and regions in which our Group operates, our business activities may be hindered.
Besides the above risks, other risks associated with global business development include changes in economic conditions in various countries and regions, unforeseen policies and regulations, and changes in our business partners' business strategies and product development.
To address these risks, the Group constantly monitors the situation and reviews business strategies and overseas investments. In addition, we respond appropriately to these changes by sharing information from local sites and cooperating with each business. Furthermore, we strive to collect information on individual country risks, such as legal regulations overseas, and share and disseminate such information within the Group. On top of this, we formulate conventional risk mitigation measures and BCPs, which are periodically reviewed.
Particularly in the Metals business, there is a risk of being affected by events beyond the control of the Group, such as intervention in resource projects by national and local governments in copper-producing countries, fluctuations in the global supply-demand balance of copper concentrates, and declining copper concentrate grades. To mitigate these risks, we promote the diversification of countries and regions where we purchase copper concentrates as well as more effective investment in superior mining projects as part of our efforts to form a sustainable raw material procurement portfolio. At the same time, we actively use recycled raw materials like E-Scrap (waste circuit boards from various electronic devices) to ensure stable supplies of raw materials.
-
(11) Financial riskLikelihood of occurrence: Medium; Impact: Large
- Interest-bearing debt
As of March 2024, the Group's interest-bearing debt (sum of short-term borrowings, commercial paper, corporate bonds, and long-term borrowings; unless otherwise noted, the same applies below) totaled ¥593.0 billion. The ratio of interest-bearing debt to total assets was 25.0%. We strive to improve our financial position by reducing inventories and selling assets; however, if financing costs rise due to future changes in the financial situation, the Group's performance and financial position could be affected.
Therefore, we maintain the balance of interest-bearing debt and net debt-to-equity ratio at appropriate levels, ensure a variety of financing methods, and raise funds in a timely and appropriate manner, thereby reducing financing costs. We are committed to improving cash efficiency by introducing a cash management system to centralize the management of surplus funds at each Group company.
- Changes in the market value of assets held
Fluctuations in the market value of securities, land, and other assets held by the Group may affect its performance and financial position.
For this reason, the Group periodically checks the market value of securities and the financial status of issuers and continually reviews the status of holdings in light of the relationship with issuers. Regarding the impairment of fixed assets, we proceed with selling idle land, and as for business assets, we obtain real estate appraisals as needed and determine whether there are indications of impairment.
- Response to increased working capital and deterioration of capital efficiency due to rising metal prices
An increase in the price of metals, including copper, may lead to an increase in mine dividends and other benefits, but it may also lead to an increase in working capital and a deterioration in capital efficiency within the Group.
Accordingly, we are working to improve capital efficiency by reducing inventories and other means.
- Retirement benefit expenses and liabilities
Retirement benefit expenses and liabilities for employees are calculated mainly based on actuarial assumptions. These assumptions take into account the average remaining years of service of employees, the long-term yield of Japanese government bonds, and the status of pension asset management, including trust contribution shares. However, a decline in the discount rate and losses arising from pension asset management could affect the Group's future expenses and liabilities to be allocated.
Therefore, the Group has introduced a retirement benefit plan that combines defined benefit and defined contribution plans, as well as appropriate investment allocation that considers safety and profitability in pension asset management.
- Interest-bearing debt
-