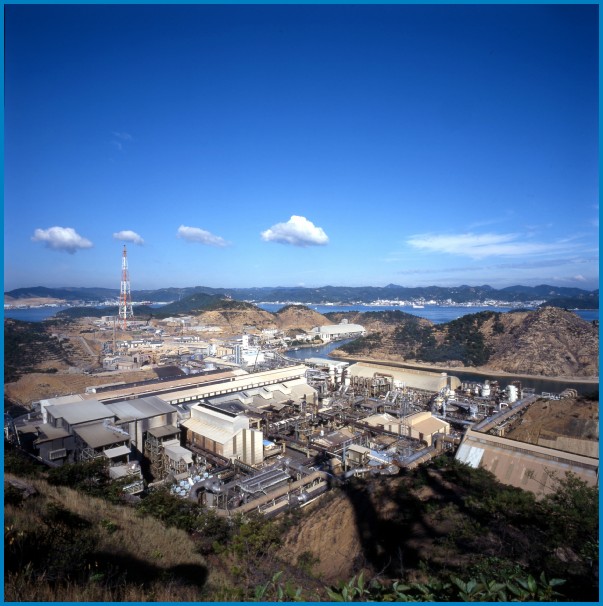

Aerial View of Naoshima Smelter and Refinery |
Naoshima Smelter and Refinery is Mitsubishi
Materialsf flagship smelter, and can trace
its roots back to 1918 when operations first
started using a reverberatory furnace. Naoshima
is located in the middle of the scenic Seto
Inland Sea National Park, and has strict
environmental regulations. In 1959, development of the Mitsubishi Process began, and in 1974 the first commercial scale Mitsubishi Process Smelter began operating in Naoshima with an anode production capacity of 48,000 t/y. This was doubled to 96,000 t/y in 1982, by increasing oxygen enrichment. In 1991, the existing reverberatory + PS converter line and original Mitsubishi Process line were halted and consolidated into one new larger Mitsubishi Process line with production capacity of 204,000 t/y. This was subsequently increased to 240,000 t/y one year later. In 2000 with no change to furnace dimensions, but merely increasing oxygen enrichment, production was lifted above 270,000 t/y. |
Naoshima continues to act as a vital resource
to all other Mitsubishi operations in terms
of furnace design, process data, plant practice
and process control.
The main features of Naoshima's operations
are:
 |
The Mitsubishi Process Smelter Building at Naoshima |
 |
Naoshima' Smelter Control Room |
The figure below shows a detailed arrangement of the current Mitsubishi Process Plant and ancillary equipment at Naoshima.
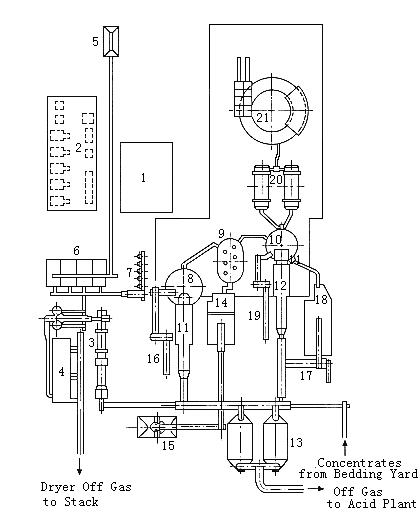 |
1.Control Room 2.Compressor Room 3.Dryer 4.Bag House 5.Flux Receiving Hopper 6.Flux Bins 7.Feeding Tanks for Smelting Furnace 8.Smelting Furnace 9.Slag Cleaning Furnace 10.Converting Furnace 11,12.Boilers 13.Electrostatic Precipitators 14.Discard Slag Granulation Pit 15.Slag Bin 16.Pressed Scrap Conveyor 17.C-Slag Dryer 18.C-Slag Granulation Pit 19.Anode Scrap Conveyor 20.Anode Furnaces 21.Casting Wheel |
The table below shows a comparison between initial design and current operating parameters of Naoshima's Mitsubishi Process Smelter.
| Design | Current | ||
| S Furnace Concentrates Coal Return C-slag |
T/H T/H T/H |
85.0 2.3 7.0 |
91.3 3.0 10.0 |
|
Nm3/h Nm3/h Nm3/h % |
24,000 16,100 40,100 45.0 |
13,900 18,800 32,700 55.2 |
| C Furnace Matte Anode scrap Return C-slag |
T/H T/H T/H |
43 4.6 2 |
56.8 5.0 18.5 |
|
Nm3/h Nm3/h Nm3/h % |
19,700 4,300 24,000 32.0 |
22,500 7,500 30,000 36.2 |
| Offgas S-furnace C-furnace |
DNm3/min SO2% DNm3/min SO2% |
620 30.0 390 27.0 |
500 37.7 480 28.0 |
| Anode Production from concentrate from scrap |
T/Y T/Y |
192,000 12,000 |
265,000 13,000 |
| Total production (from new source) |
T/Y | 204,000 | 278,000 |